Detection of Syringes
Inspection Requirements:
1, Visual inspection of syringe springs and rubber rings
2, The beat is 1 unit every 2.5 seconds
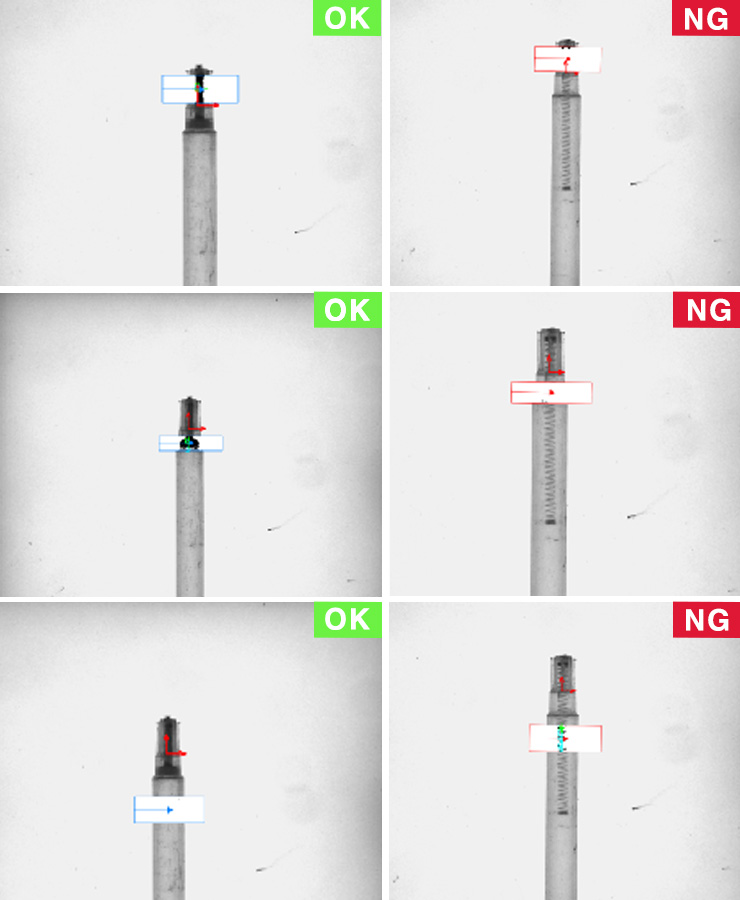
Project Details:
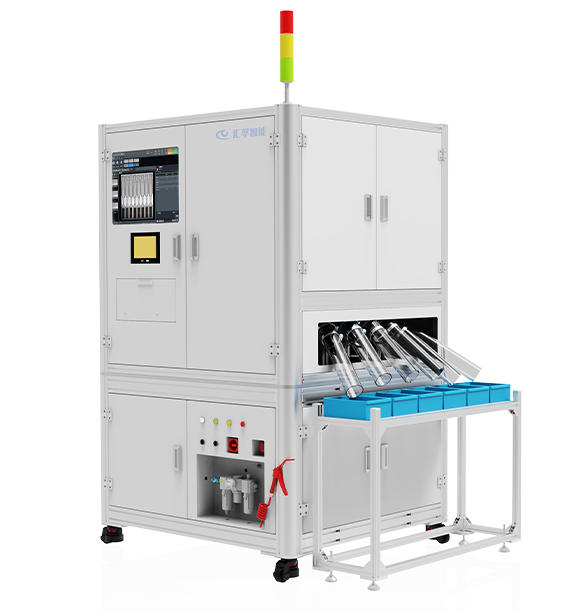
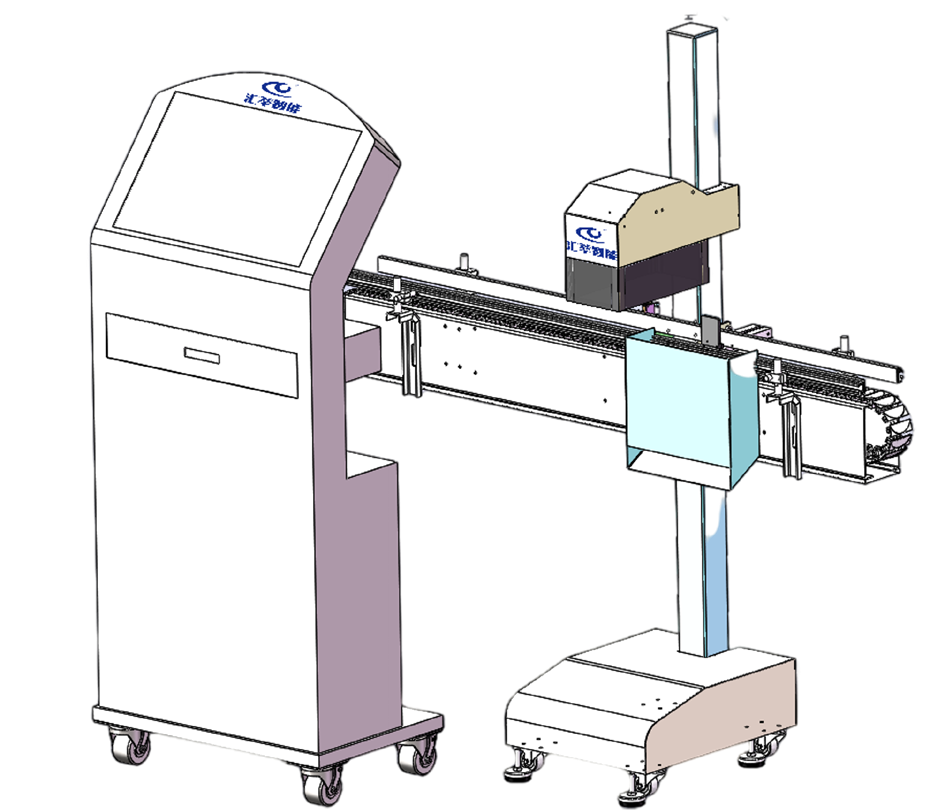
In the manufacturing process of medical devices, the springs and rubber rings of syringes are critical components that influence both elasticity and sealing effectiveness. Any oversight in the assembly of these parts could render the syringe inoperative, thereby jeopardizing patient safety. Traditional manual inspection methods, when faced with large-scale production, are prone to errors or omissions, making it challenging to maintain high precision. Consequently, a certain medical equipment manufacturer has adopted an automated inspection system based on machine vision to ensure the proper assembly of springs and rubber rings.
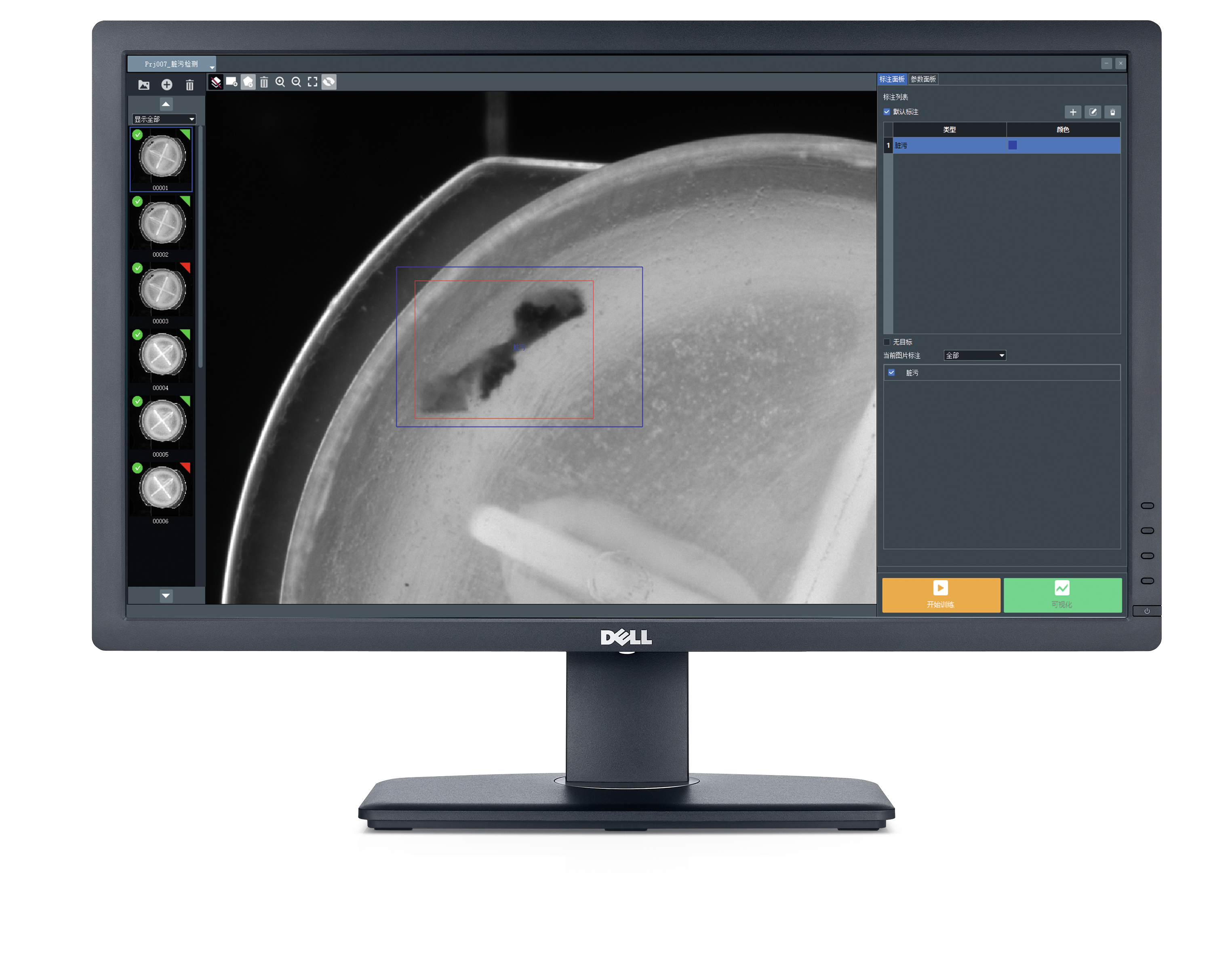
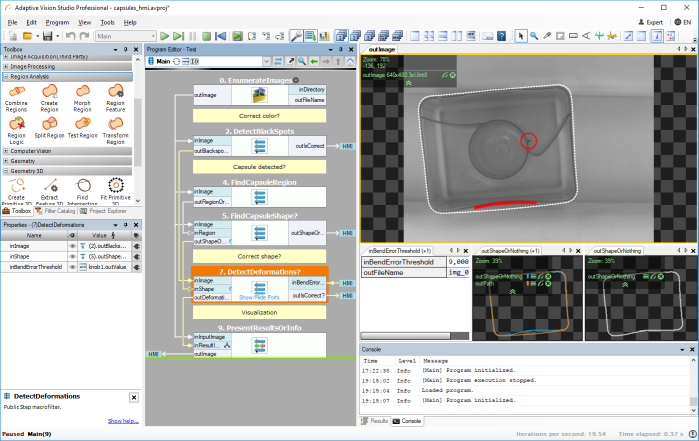
The introduction of machine vision has significantly enhanced the efficiency of the production line and elevated quality control standards. The system is equipped with high-resolution industrial cameras that can capture minute internal details of syringes in a remarkably brief period, clearly displaying the assembly status of the springs and rubber rings. Additionally, intelligent image processing algorithms analyze and identify the captured images, swiftly determining the presence of springs and rubber rings and verifying their correct assembly. Whether it involves misaligned springs, absent rubber rings, or other anomalies, the system can detect these issues instantaneously.
Furthermore, the system features a rapid feedback mechanism; upon identifying an improperly assembled syringe, it promptly issues an alert and removes the defective product from the production line via an automatic ejection device, ensuring that substandard items do not progress to subsequent stages. This not only enhances inspection accuracy but also significantly reduces the rates of false positives and omissions in manual inspections, guaranteeing that every syringe entering the market is fully functional and safe.