In machine vision systems, lens selection is essential to effective image capture, directly influencing the system’s overall performance. A carefully chosen lens maximizes efficiency, accuracy, and reliability by capturing light accurately and delivering high-quality image data for analysis. This guide outlines key considerations for selecting lenses in industrial applications, covering lens types, classifications, and critical parameters.
Key Considerations for Industrial Lens Selection
Before selecting an industrial lens, keep these points in mind:
- Telecentric Lens Requirement: Determine if a telecentric lens is needed to minimize perspective errors.
- Filter Requirement: Confirm if the application requires an optical filter.
- Depth of Field: Ensure sufficient depth of field for consistent image clarity.
- Camera Sensor Compatibility: Check that the lens is compatible with the camera’s sensor.
- Lens Mount Compatibility: Verify that the lens mount matches the camera interface.
- Minimum Working Distance: Define the closest working distance required.
- Focal Length: Set the focal length for the desired field of view.
- Distortion: Consider if lens distortion will affect inspection accuracy.
Types of Industrial Lenses
1. By Focal Length: Fixed vs. Zoom Lenses
- Fixed-Focal Lenses: Provide a fixed focal length with an adjustable aperture, offering high image quality and minimal distortion at short working distances.
- Zoom Lenses: Allow continuous adjustment of focal length for applications requiring variable object distances, though they may be larger and offer slightly lower image quality than fixed lenses.

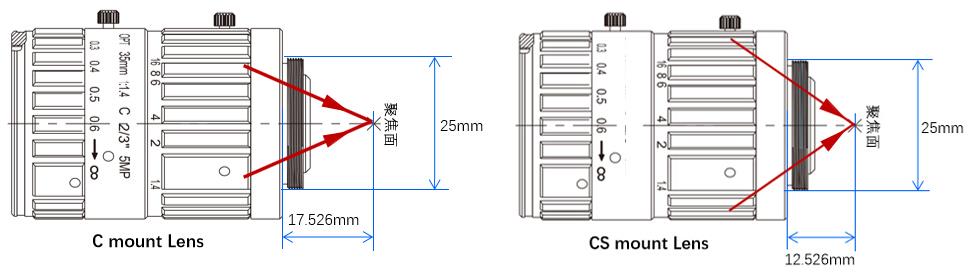
2. By Lens Interface: C-Mount and CS-Mount
- C-Mount: Widely used due to its compactness, lightweight design, and economic efficiency, with a 17.5 mm flange focal distance.
- CS-Mount: Converts to a C-mount with a 5 mm extension ring, offering versatile compatibility.
3. Specialty Lenses
- Microscope Lenses: Suited for high magnification, typically above 10:1 or 2:1 in high-resolution applications.
- Macro Lenses: Ideal for magnifications between 2:1 and 1:4, commonly used in close-up inspections.
- Telecentric Lenses: Designed to minimize perspective distortion, maintaining consistent magnification across different object distances, ideal for non-flat surfaces.

4. By Light Wavelength: Infrared and Ultraviolet Lenses
- Infrared Lenses: Correct chromatic aberrations specific to IR wavelengths.
- Ultraviolet Lenses: Optimized for UV light, useful in specialized inspection settings.
Essential Lens Parameters
1. Focal Length
Focal length determines working distance, image scale, and field of view. Typical focal lengths range from 4 mm to 75 mm.
2. Aperture
The aperture size (f-number) defines the lens’s light-gathering ability and impacts depth of field. It is calculated as the ratio of effective focal length to aperture diameter.
3. Working Distance
Working distance is the space from the lens’s front element to the object, influencing the field of view.
4. Field of View (FoV)
FoV, or the observable area in the camera’s frame, depends on sensor size and lens magnification. Select a lens with an FoV slightly larger than the object for inspection.
5. Magnification
Telecentric lenses have a fixed magnification, requiring a fixed installation height. Optical magnification is calculated as:
6. Resolution
Resolution, measured in line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm), defines image detail quality. Higher resolution enhances clarity.
7. Depth of Field
Depth of field refers to the in-focus range within an image. Smaller apertures increase depth of field, while larger apertures reduce it.
8. Distortion
Distortion refers to image warping, particularly in wide-angle lenses. For high-accuracy applications, telecentric lenses significantly reduce distortion.

Why Choose MSTAR TECHNOLOGIES for Machine Vision Solutions?
MSTAR TECHNOLOGIES, a leader in machine vision technology, provides end-to-end solutions for diverse industrial applications. Our HCvisionQuick software, integrated with a comprehensive hardware lineup—including processors, cameras, lighting, lenses, and accessories—ensures high-precision, reliable machine vision solutions. For machine vision needs, MSTAR TECHNOLOGIES offers advanced technology, expertise, and professionalism, setting the standard for quality and innovation.