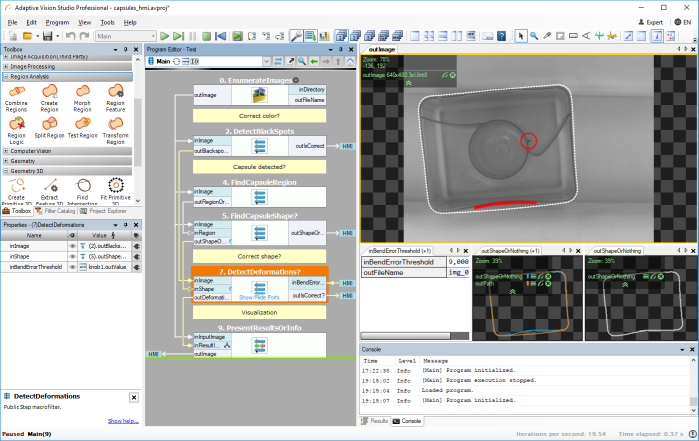
What is 3D Machine Vision Inspection?
3D machine vision inspection is an advanced technology that combines multi-dimensional image analysis with point cloud data to enable precise detection and positioning. By capturing depth data from varied angles, it integrates geometric and color attributes to recognize and measure targets. Essentially, 3D machine vision inspection serves as a substitute for human visual assessment, utilizing image capture devices like CMOS or CCD sensors that convert a target into digital image signals. These signals are transmitted to an image processing system, which analyzes pixel distribution, brightness, and color to extract features, automating equipment adjustments based on inspection results. This capability is invaluable in manufacturing, assembly, and packaging, enhancing defect detection and ensuring only quality products reach consumers.
The flexibility and automation afforded by 3D machine vision inspection make it indispensable, especially in environments hazardous for human operators or where human inspection alone is insufficient. In large-scale production, human inspection is not only inefficient but often lacks the precision needed. In contrast, machine vision inspection significantly enhances production efficiency and consistency. Additionally, machine vision enables seamless integration of data, forming a foundational technology for computer-integrated manufacturing.
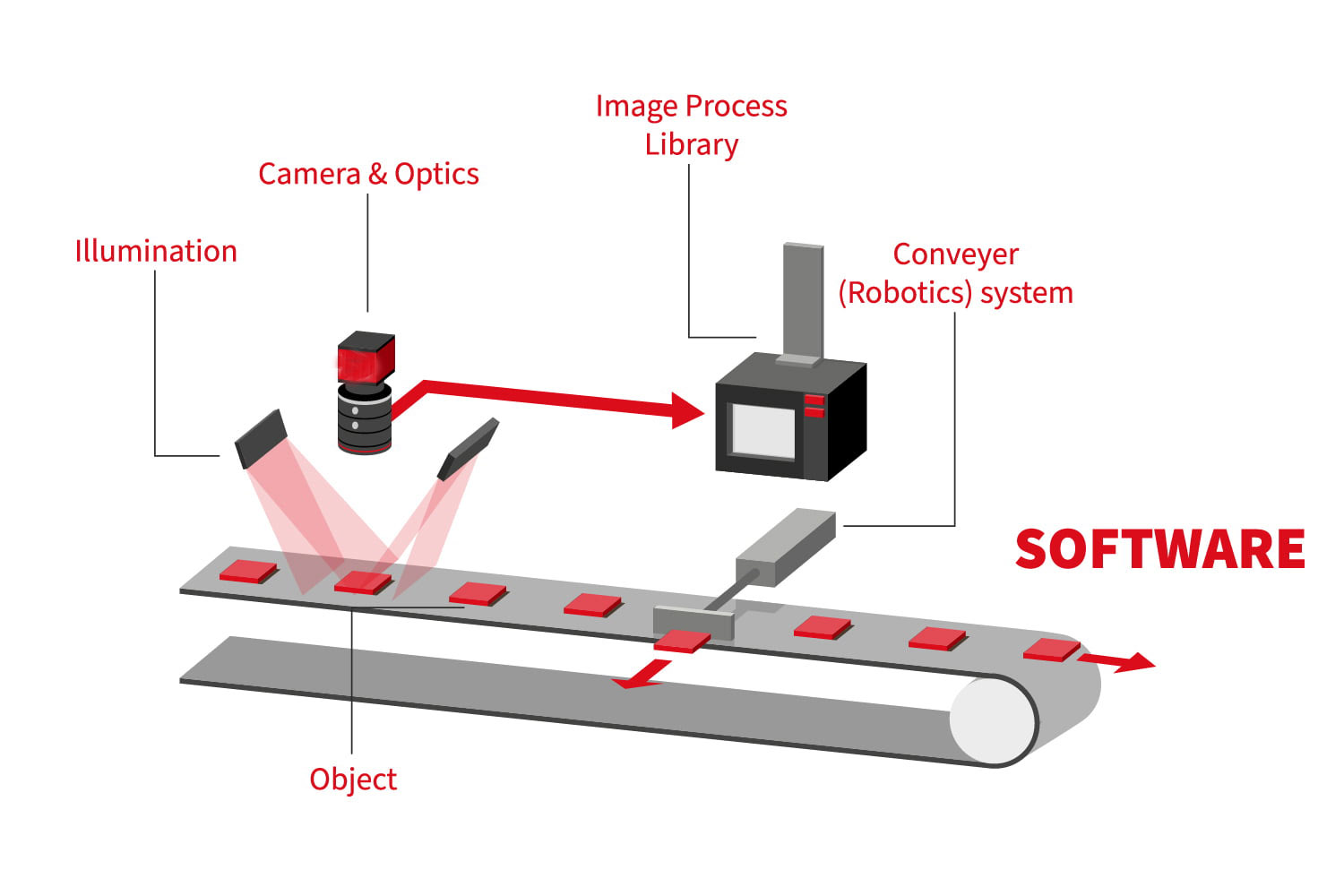
Structure and Principles of 3D Machine Vision Inspection
A typical industrial machine vision system comprises digital image processing, mechanical and control engineering, lighting, optical imaging, sensor technology, video processing, software, and human-machine interface technology.
Image Capture
The camera captures an electronic image of the object and sends it to the processor for analysis. The image is digitized into pixels, with resolution increasing as pixel count rises, thus enhancing detection precision.Camera Variables
Aperture, contrast, and shutter speed are calibrated in the inspection system to optimize image clarity, ensuring accurate detection.Lighting Component
Effective lighting is essential for creating contrast. Designers invest considerable time selecting lighting types, angles, colors, and intensities to achieve optimal detection contrast.Software Tools
Vision inspection systems utilize software to process images using algorithmic tools that aid in analysis. These tools perform tasks such as search, edge detection, feature analysis, and visual print inspection, ensuring thorough inspections.

Key Advantages of 3D Machine Vision Inspection
High Precision
While human vision operates on limited grayscale levels, machine vision offers enhanced grayscale depth and resolution, enabling micron-level observation and detection.High Speed
Machine shutters operate at microsecond speeds, capturing rapid motions that are beyond human perceptual limits.Superior Stability
Machine vision eliminates human error in manual inspection, as it performs consistently without fatigue or emotional influence, greatly enhancing quality control.Data Integration and Retention
Machine vision gathers a substantial and traceable dataset, allowing for seamless data integration and secure retention for analysis and future reference.

Applications of 3D Machine Vision Inspection
Printing Industry
Both online and offline, 3D machine vision systems detect quality issues like die-cutting misalignments, ink smudging, misregistration, and color variations. Real-time feedback to the PLC enables dynamic ink adjustments, improving print quality and efficiency.PCB Inspection
Vision systems inspect bare PCBs, detecting misplacements, spacing errors, incorrect component dimensions, shape inconsistencies, circuit continuity, and contaminants, ensuring precision in PCB manufacturing.Metal Parts Inspection
Machine vision enhances quality control in metal parts production by identifying defects like scratches, discoloration, and residual films. Defective items are swiftly removed, increasing production efficiency and enabling targeted quality improvements.Automotive Safety
Machine vision monitors drivers' eyelids, gaze, and head orientation to detect fatigue, enhancing road safety through real-time, model-based fatigue analysis.Metal Surface Defect Control
Machine vision detects metal surface defects with high-speed, precise inspection. The non-contact measurement prevents new scratches, while line-scan CCD technology captures 3D images as metal sheets move along the production line.
3D machine vision inspection is transforming industries by enabling high precision, speed, stability, and data integration, ensuring quality control and operational efficiency across numerous applications. From manufacturing to public safety, this technology is shaping the future of automation and industrial inspection.